Quantitative Marktforschungsmethoden

Quantitative market research is a cornerstone of modern business strategy – and it provides valuable data that helps organizations understand their markets, customers, and competitors. By using structured methods and statistical techniques, businesses can gather and analyze large volumes of data, enabling them to make informed decisions that drive growth and profitability.
Some of the most critical methods of quantitative market research are:
Survey Research in Quantitative Market Research
Survey research is one of the most widely used techniques in quantitative market research. It offers a straightforward way to collect data from many respondents.
Types of Surveys
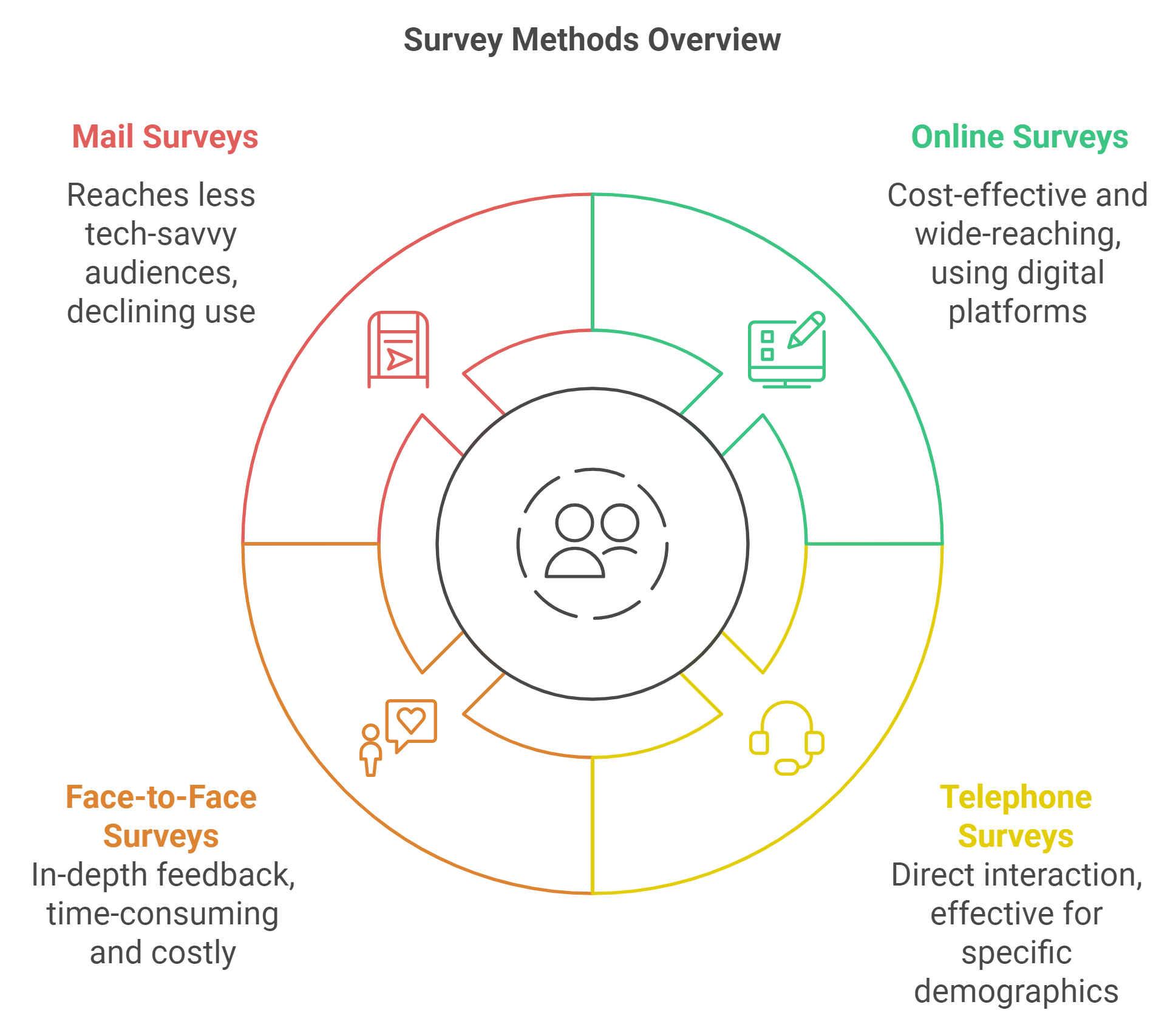
- Online-Umfragen: These are popular due to their cost-effectiveness and ability to reach a wide audience quickly. They can be distributed via email, social media, or embedded on websites. Tools like Google Forms, SurveyMonkey, and Qualtrics make creating and analyzing online surveys accessible to businesses of all sizes.
- Telephone Surveys: Although less common today, telephone surveys are still effective for reaching specific demographics, especially older adults. They offer the advantage of real-time interaction, allowing for clarification of responses.
- Face-to-Face Surveys: These are often used in public places or events to gather immediate feedback. While they can be time-consuming and expensive, face-to-face surveys allow a deeper understanding of respondent reactions.
- Mail Surveys: Though declining in use, mail surveys can help reach less tech-savvy audiences or areas with limited internet access. They typically include incentives to encourage response rates.
Best Practices for Designing Effective Surveys
- Keep it Short and Focused: Long surveys can fatigue respondents, resulting in incomplete data or drop-offs. Aim for clarity and brevity, focusing on critical questions that align with your research objectives.
- Use Clear and Unbiased Language: Avoid leading or loaded questions that might influence responses. Neutral wording ensures that the data collected reflects accurate opinions and behaviors.
- Pilot Test Your Survey: Before launching a survey, conduct a pilot test with a small group to identify issues with question clarity, survey flow, or technical glitches. This helps in refining the study for better data collection.
- Incentivize Participation: Offering a small incentive, such as a discount, gift card, or entry into a prize draw, can significantly boost response rates.
For instance, a fashion retailer might use an online survey to understand customer preferences for new seasonal collections. By asking specific questions about color, style, and price points, the retailer can tailor its inventory to meet customer demands.
Experimental Research in Quantitative Market Research
Experimental research is a powerful technique in quantitative market research that allows businesses to test hypotheses and measure the impact of different variables on consumer behavior.
Key Concepts in Experimental Research
- Control Groups and Variables: In experimental research, participants are often divided into a control group and one or more experimental groups. The control group is exposed to standard conditions, while the experimental group experiences a variation of interest. This setup helps isolate the effect of the tested variable, ensuring that any observed changes can be attributed to that variable.
- Independent and Dependent Variables: The independent variable is the factor that is manipulated in the experiment (e.g., price change, advertisement style), while the dependent variable is the outcome that is measured (e.g., sales, customer engagement). Understanding this relationship is crucial for designing experiments that yield actionable insights.
Common Experimental Designs
- A/B Testing: A/B testing is a popular method where two versions of a product, webpage, or marketing campaign are compared to see which performs better. For example, an e-commerce site might test two different homepage designs to determine which one leads to higher conversion rates.
- Randomized Control Trials (RCTs): RCTs are the gold standard in experimental research, particularly in healthcare and social sciences sectors. Participants are randomly assigned to either the control or experimental group, reducing bias and ensuring the validity of the results.
- Pre-Test/Post-Test Design: In this design, measurements are taken before and after an intervention to assess its impact. For instance, a company might measure customer satisfaction before and after implementing a new customer service training program.
Actionable Tips for Conducting Experimental Research
- Define Clear Objectives: Before starting an experiment, clearly define your aim. This includes identifying the independent and dependent variables and setting measurable goals.
- Ensure Adequate Sample Size: A small sample size can lead to unreliable results. Use statistical tools to calculate the required sample size to ensure your findings are statistically significant.
- Minimize Bias: Ensure that the participants are randomly assigned to control and experimental groups, and keep conditions consistent across groups except for the variable being tested. This reduces the risk of bias influencing the results.
- Monitor and Adjust: Monitor the results closely as the experiment progresses. If unexpected issues arise, be prepared to adjust the experiment or conduct additional tests to validate findings.
For example, a beverage company could use experimental research to test the impact of different packaging designs on consumer preference. The company can identify which packaging option resonates most with its target audience by controlling variables such as color, shape, and labeling.

Data Analytics and Statistical Techniques
Data analytics and statistical techniques are essential components of quantitative market research. These methods allow businesses to process and interpret vast amounts of data, uncovering patterns and insights that inform strategic decisions. By applying the right statistical tools, companies can transform raw data into actionable information, driving better marketing, sales, and product development outcomes.
Key Statistical Techniques
- Regression Analysis:
- Regression analysis is used to identify relationships between variables. For example, it can help determine how price changes affect sales or how advertising spend influences brand awareness.
- Factor Analysis:
- Factor analysis reduces large datasets into smaller sets of underlying factors. This is particularly useful when dealing with survey data where multiple variables might be correlated.
- Cluster Analysis:
- Cluster analysis groups data into clusters based on similarity. It’s commonly used for market segmentation, where businesses want to identify distinct customer groups with similar characteristics.
- Conjoint Analysis:
- Conjoint analysis is used to understand how consumers value different product or service attributes. It helps identify the most important features that drive purchase decisions.
- Conjoint analysis is used to understand how consumers value different product or service attributes. It helps identify the most important features that drive purchase decisions.
Sampling Methods in Quantitative Market Research
Sampling methods are crucial in quantitative market research as they determine how representative and reliable your data will be.
Overview of Sampling Techniques
- Random Sampling:
- Random sampling ensures that everyone in the population has an equal chance of being selected, reducing bias and improving the sample’s representativeness.
- Stratified Sampling:
- Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into distinct subgroups (strata) and sampling from each subgroup. This method ensures that specific segments of the population are adequately represented.
- Cluster Sampling:
- Cluster sampling involves dividing the population into clusters (e.g., geographic areas) and then randomly selecting whole clusters to participate. This method is often used when a population is spread out over a large area.
- Cluster sampling involves dividing the population into clusters (e.g., geographic areas) and then randomly selecting whole clusters to participate. This method is often used when a population is spread out over a large area.
Choosing the Right Sampling Method
- Define Your Objectives: The choice of sampling method should align with your research objectives and the specific characteristics of the population you’re studying. Consider factors such as the size and diversity of the population, available resources, and desired level of accuracy.
- Calculate Sample Size: Use statistical formulas to determine the appropriate sample size for your research. A larger sample size generally provides more accurate results and requires more resources. Balance the need for precision with practical considerations.
- Consider Cost and Logistics: Different sampling methods have varying costs and logistical requirements. For example, stratified sampling may require more detailed planning and data on population segments, while cluster sampling may reduce survey costs by focusing on specific areas.
Data Interpretation and Reporting
Data interpretation and reporting are critical techniques in quantitative market research that transform raw data into actionable insights.
Daten analysieren
- Descriptive Statistics:
- Descriptive statistics summarize and describe the main features of a dataset, including measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and measures of dispersion (range, variance, standard deviation).
- Inferential Statistics:
- Inferential statistics are used to make inferences and draw conclusions about a population based on a sample. Techniques include hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and correlation analysis.
- Data Modeling:
- Data modeling involves creating statistical models to understand relationships between variables and predict future outcomes. Common models include linear regression, logistic regression, and time series analysis.
Reporting Findings
- Creating Clear Visualizations:
- Visualizations such as charts, graphs, and tables help present data in a way that is easily understandable and interpretable. They can reveal trends, patterns, and relationships that might not be immediately apparent from raw data.
- Crafting a Comprehensive Report:
- A comprehensive report summarizes the research objectives, methods, findings, and implications. It provides a structured overview of the research and recommendations for action.
- Presenting Insights Effectively:
- Effective presentation of insights ensures that stakeholders understand and can act on the research findings. This may involve presenting results in meetings, workshops, or written summaries.
- Effective presentation of insights ensures that stakeholders understand and can act on the research findings. This may involve presenting results in meetings, workshops, or written summaries.
How SIS International Helps Businesses Choose the Right Methods and Techniques in Quantitative Market Research
At SIS International, we understand that choosing the right techniques in quantitative market research is essential for businesses aiming to make data-driven decisions. Our approach is rooted in decades of experience and a deep understanding of global markets, allowing us to tailor research methods to each client’s specific needs and objectives.
Customized Methodology:
Bei SIS International, we recognize that every business has unique challenges and goals. Our team works closely with clients to develop a customized research methodology that aligns with their objectives.
Strategic Sampling Selection:
We help businesses select the most appropriate sampling techniques to ensure their research is reliable and representative. Our experts consider the target population, research objectives, and available resources to recommend the most effective sampling method.
Innovative Data Collection:
SIS International utilizes various data collection techniques to gather accurate and relevant data. From traditional surveys and experiments to cutting-edge digital tools, we ensure the data collection process is efficient and effective.
Sophisticated Analytics:
Our data scientists and analysts are skilled at applying advanced statistical methods to interpret complex data sets. We use various analytical techniques to uncover actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making, including regression analysis, factor analysis, and predictive modeling.
Clear and Actionable Reporting:
SIS International emphasizes the importance of clear and actionable reporting. We present research findings in a way that is easy to understand and directly relevant to our clients’ strategic goals. Our reports include detailed visualizations, executive summaries, and practical recommendations that enable businesses to take informed action.
Understanding Regional Nuances:
With a global presence and deep local expertise, SIS International helps businesses navigate the complexities of international markets. We understand the cultural, economic, and regulatory factors influencing market research in different regions, ensuring our clients receive globally informed and locally relevant insights.
Über SIS International
SIS International bietet quantitative, qualitative und strategische Forschung an. Wir liefern Daten, Tools, Strategien, Berichte und Erkenntnisse zur Entscheidungsfindung. Wir führen auch Interviews, Umfragen, Fokusgruppen und andere Methoden und Ansätze der Marktforschung durch. Kontakt für Ihr nächstes Marktforschungsprojekt.


